Why Reciprocating Engines Remain Essential in Marine Propulsion
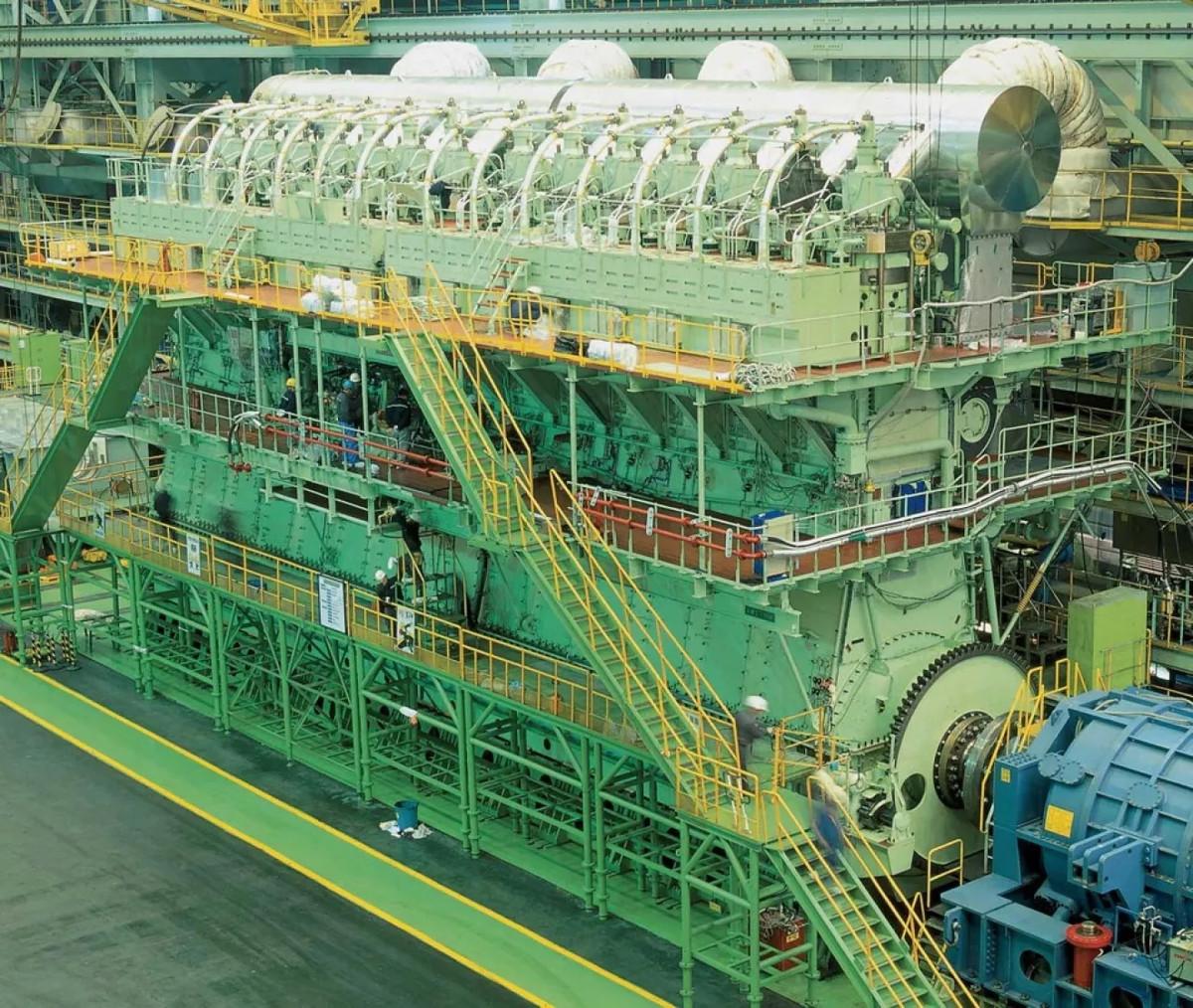
Introduction
The Marine Reciprocating Engine Market is growing steadily as global maritime operations expand across commercial shipping, offshore activities, naval fleets, and recreational boating. Reciprocating engines—also known as piston engines—convert fuel combustion into mechanical power to propel vessels of various sizes, including cargo ships, fishing boats, ferries, tugboats, patrol vessels, and yachts. These engines remain widely used due to their high torque output, operational efficiency, fuel flexibility, and ease of maintenance. As maritime trade continues to rise and fleets modernize, reciprocating engines play a critical role in ensuring reliable propulsion and auxiliary power generation.
Market Drivers
A major driver of this market is the sustained growth of global seaborne trade, which relies heavily on durable and fuel-efficient propulsion engines. Reciprocating engines are preferred in small to medium-sized vessels due to their excellent load-handling capability and ability to operate efficiently at variable speeds. Increasing offshore oil and gas operations drive demand for engines used in supply vessels, crew boats, and anchor-handling tugs. The expansion of fishing fleets and coastal tourism boosts adoption in leisure and commercial boats. Rising focus on fuel efficiency and lower emissions encourages the development of upgraded reciprocating engines with improved combustion and optimized fuel injection systems.
Market Challenges
Despite strong demand, the Marine Reciprocating Engine Market faces challenges related to environmental compliance and emission regulations. IMO (International Maritime Organization) sulfur limits and NOx reduction norms require engine upgrades, retrofits, or the integration of exhaust treatment systems. Reciprocating engines running on conventional marine fuels must adapt to cleaner alternatives such as LNG, biofuels, methanol, and low-sulfur marine gas oil. High maintenance requirements in harsh maritime environments pose operational challenges. Fuel price volatility impacts running costs. Smaller ship operators may struggle with the capital investment needed to upgrade engines or adopt hybrid propulsion systems. Supply chain disruptions can also affect engine availability and spare part supply.
Market Opportunities
There are major opportunities in the development of dual-fuel reciprocating engines capable of operating on LNG, hydrogen blends, methanol, or ammonia. Hybrid propulsion systems combining reciprocating engines with electric motors and battery storage offer strong growth potential for ferries, tugboats, and coastal vessels. The rise of autonomous and smart ships presents opportunities for digitally monitored engines with predictive maintenance and advanced diagnostics. Retrofitting older vessels with low-emission reciprocating engines offers a significant aftermarket opportunity. Growth in recreational boating and luxury yachts also creates demand for compact, low-noise, and high-performance propulsion engines. Offshore wind farm service vessels present another emerging opportunity.
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific dominates the Marine Reciprocating Engine Market due to large shipbuilding industries in China, South Korea, and Japan. Southeast Asia shows strong adoption in fishing fleets and inter-island transport. Europe demonstrates steady demand driven by green shipping initiatives, ferry electrification, and offshore wind support vessels. North America sees increasing usage in coastal shipping, naval applications, and recreational boating. The Middle East expands demand through oil and gas maritime logistics, while Latin America shows rising adoption across fishing fleets and port operations. Africa presents long-term opportunities as coastal trade and marine infrastructure grow across West and East African nations.
Future Outlook
The future of the Marine Reciprocating Engine Market will be shaped by cleaner fuels, hybrid propulsion adoption, and digital engine management systems. Engines designed for carbon-neutral fuels such as green methanol, bio-LNG, and ammonia will gain prominence. Advancements in turbocharging, fuel injection, and thermal efficiency will enhance performance. Integration of IoT and AI technologies will enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote diagnostics. Hybrid-electric reciprocating engines will become more common in short-distance commercial fleets. As maritime emission regulations tighten globally, manufacturers will focus on advanced low-emission reciprocating engines that balance efficiency and sustainability.
Conclusion
The Marine Reciprocating Engine Market continues to expand as global maritime trade, offshore operations, and recreational boating drive demand for reliable propulsion systems. Despite challenges related to emission norms, maintenance requirements, and fuel transitions, strong growth arises from fleet modernization, hybrid technology adoption, and emerging clean fuel alternatives. Innovations in engine efficiency, dual-fuel systems, and digital monitoring will shape the future of reciprocating marine engines. As coastal transport and ocean-based industries evolve, reciprocating engines will remain essential for powering versatile and dependable marine vessels.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Игры
- Gardening
- Health
- Главная
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Другое
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
