The Future of Carbon Credits: Paving the Way to Net Zero
Introduction
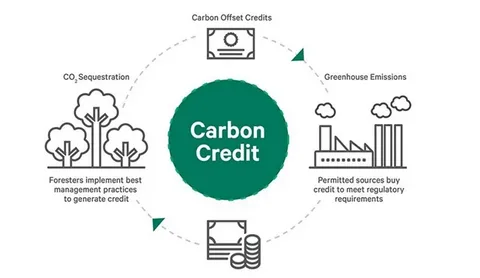
The Carbon Offset/Carbon Credit Market has emerged as a crucial mechanism in the global fight against climate change. As nations, corporations, and industries strive to achieve net-zero emissions, carbon credits enable them to offset unavoidable emissions through verified projects that reduce, remove, or prevent greenhouse gases. The market, valued in billions, is expanding rapidly as both compliance and voluntary participants adopt greener policies and integrate sustainability into their business operations. With growing awareness and supportive regulatory frameworks, the carbon credit ecosystem is set to redefine how businesses perceive environmental accountability and economic growth.
Market Drivers
A major driver of this market is the rising corporate commitment toward carbon neutrality. Global companies like Microsoft, Amazon, and Shell are increasingly investing in carbon credits to balance their carbon footprint. The expansion of cap-and-trade programs and national carbon pricing mechanisms has also accelerated adoption. Moreover, the increasing focus on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investments is encouraging industries and investors to buy carbon credits, boosting demand in both voluntary and compliance markets. Additionally, the growth of nature-based solutions such as reforestation, afforestation, and soil carbon sequestration is enhancing the quality and supply of carbon credits.
Market Challenges
Despite rapid growth, the market faces several challenges. One key issue is lack of transparency and standardization. With multiple certification agencies and methodologies, ensuring the authenticity of carbon credits can be complex. The double-counting problem, where the same credit is claimed by multiple entities, reduces credibility. Furthermore, the volatility in carbon prices creates uncertainty for investors. Another concern is greenwashing, where companies rely heavily on offsets instead of genuinely reducing emissions. Regulatory gaps in voluntary carbon markets, as well as limited awareness in developing economies, also hinder large-scale participation.
Opportunities
Opportunities in the carbon credit market are vast and multi-dimensional. The global push toward net-zero emissions by 2050 is driving both innovation and investment. Technologies like blockchain-based verification systems promise to enhance traceability and credibility in carbon transactions. The expansion of carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) projects and renewable energy initiatives opens new sources for credit generation. Additionally, cross-border carbon trading platforms and regional cooperation in emission reduction could create new revenue streams for developing countries. Companies providing carbon measurement and verification services are also expected to see rising demand.
Regional Insights
Regionally, Europe leads the global carbon credit market due to stringent emission norms and its well-established EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS). North America follows, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and state-level programs like California’s Cap-and-Trade. The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing significant potential, with countries such as China and India launching domestic carbon markets. China’s national ETS, one of the largest in the world, represents a major leap toward emission control. In contrast, Africa and Latin America are becoming key suppliers of nature-based carbon credits through reforestation and renewable energy projects.
Future Outlook
The future of the carbon offset market looks promising as more nations and industries commit to carbon neutrality. Technological advancements in digital MRV (Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification) and AI-driven emission tracking will enhance credibility. The expansion of global carbon pricing frameworks, coupled with integration of carbon credits into financial portfolios, could make them a mainstream investment asset. Furthermore, greater alignment between voluntary and compliance markets will create a more unified and transparent ecosystem. By 2030, the market could become one of the key pillars in global climate financing and sustainable development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Carbon Offset/Carbon Credit Market is not just an environmental initiative—it’s a transformative economic tool reshaping global sustainability efforts. While challenges in verification and regulation persist, the overall momentum toward decarbonization ensures a robust future. Businesses adopting a balanced approach—combining emission reduction and credible offsetting—will play a central role in achieving a net-zero world. The path ahead involves collaboration, innovation, and transparency to make carbon trading a trusted pillar of climate action.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Игры
- Gardening
- Health
- Главная
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Другое
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
